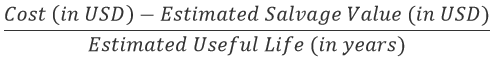Useful Terms Related to Accounting and Tax
This page is dedicated to provide you with all the terms that are frequently used in accounting and tax topics to make sure that you find everything you are looking for on our website.
Back Taxes*: are the taxes that were due but not paid by the deadline.
Bookkeeping: recording of the financial transactions for a business.
*Did you know? Ultimate Tax Relief has partnered with SharfPointers Financial Services to provide you with bookkeeping services!
C-Corporation: a type of entity in which the shareholders or the owners and the entity are taxed separately from one another.
Cryptocurrency: a digital currency that is secured by a technique called cryptography which secures communications between senders and recipients from third party entities.
Currently-Not-Collectible: a status given to a taxpayer when the IRS decides that the taxpayer is unable to pay his taxes; the taxpayer will not be asked to pay his due taxes until his financial situation improves.
Declining Balance Depreciation: a method of depreciation used for assets that lose their value faster during their earlier years; this method writes off a larger portion in the assets' earlier years and decreases the amount each year until the end of the asset's useful life.
Depreciation: the process of deducting the cost of an asset over its useful life; deducting a portion of the total cost each year.
*Did you know? There are different types of depreciation; each has its pros and cons for each asset that a business is in possession of. Hence, it is an accountant’s job to make sure that the best method is used for each asset.
Extension: a type of request that, upon approval by the IRS, will extend the taxpayer's filing window by, normally, six months. The extension is only for the filing date, not for the amount owed; the amount due still need to be paid on time*. Hence, this request is only advantageous for those who find it inconvenient to file by the regular deadline, not those who are suffering financially.
*Here is why you need to be careful before requesting for an extension.
FIFO: an inventory valuation method which assumes that the assets acquired first are the first ones to be sold or disposed of.
HIFO: an inventory valuation method which assumes that the assets with the highest cost basis are the first ones to be sold or disposed of.
Installment Agreement*: generally defined as a deal that a taxpayer makes with the IRS to pay what he/she owes in monthly installments rather than a lump sum.
*Here is what you need to know about Installment Agreement.
IRS Penalties: penalties imposed by the IRS on taxpayers who do not file their tax returns or pay the amount due on time.
♦ Has IRS charged you with penalties? Learn how to get rid of them here.
Levy*: refers to the seizure of current, as well as future assets to settle an unpaid debt.
*Click here to learn more about what levies are and how Ultimate Tax Relief can help you to get rid of them.
Lien*: a claim on a debtor’s asset(s) as security until the debt is paid off.
*Can't sell a property because of an IRS lien? Click here to learn how you can set yourself free with us.
LIFO: an inventory valuation method which assumes that the last assets acquired are the first ones to be sold or disposed of.
Offer in compromise*: refers to finding the middle ground with the IRS such that the taxpayer pays what they can afford to, not the entire amount.
*Here is a detailed overview on what Offer in compromise is and how it works.
Pass-through entity: a type of entity in which profits, losses, credits, and deductions “pass-through” the business entity to the owners or shareholders of the business. These types of corporations are subject to federal corporate taxes, the tax liability is also passed to the shareholders and owners.
Per-Diem Payments: the amount of money an employer pays their employee(s) to cover their expenses while on a business trip.
*Fun Fact: Per-Diem is Latin for per “per day”.
S-Corporations: a type of entity in which profits, losses, credits and deductions are passed to shareholders and the corporation will not pay federal corporate taxes.
Salvage Value: book value of an asset after all depreciation has been fully expensed. In short, it is the amount that a company expects to receive upon selling an asset at the end of its useful life.
Straight-Line Depreciation: a method of depreciation where a fixed amount is written off an asset's value over its estimated useful life. The formula used to calculate depreciation with the straight-line method is:
Substitute for Return Program: an IRS program through which the IRS files tax returns for taxpayers with unfiled tax returns without taking any deductibles or tax credits into consideration.
*It is always in your best interest to file your returns on time to avoid participating in such programs!
Sum-of-the-Years' Digits Depreciation: a type of depreciation where each year's digit(s) of the estimated useful life of an asset are summed up together; depreciation for each year is obtained through dividing of the highest digit is by the summation. For example, an asset having 4 years of useful life will be depreciated as follows: 1+2+3+4=10 > First year' depreciation will be 4/10=40%. > Second year will be 3/10=30% and so on.
Unit of Production Depreciation: a type of depreciation where depreciation of an asset depends on the production of units rather that how many years it is expected to operate.
Wage Garnishment: a process in which money is taken out of a debtor’s paycheck or bank account to settle an unpaid debt.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Phone: 800-674-4449
Email: info@ultimatetaxrelief.com
Address: 9458 Lanham Severn Road, Lanham, Maryland 20706